Facts About Sweden
Location and Geography
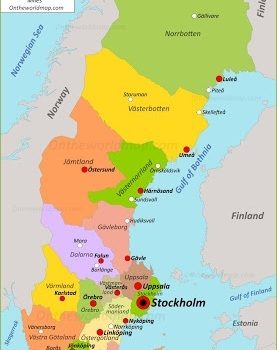

Sweden is a country in Northern Europe on the Scandinavian Peninsula. It borders Norway to the west; Finland to the northeast; and the Baltic Sea and Gulf of Bothnia to the south and east. At 450,295 km2 (173,860 sq mi), Sweden is the largest country in Northern Europe, the fifth largest in Europe, and the 55th largest country in the world.
Sweden has a 3,218 km (2,000 mi) long coastline on its east, and the Scandinavian mountain chain (Scanderna) on its western border, separating it from Norway. It has maritime borders with Denmark, Germany, Poland, Russia, Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia, and it is also linked to Denmark (southwest) by the Öresund bridge.
History and Population
Sweden, officially the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, Finland to the east, and is connected to Denmark in the southwest by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund Strait. At 450,295 square kilometers (173,860 sq mi), Sweden is the largest country in Northern Europe, the third-largest country in the European Union and the fifth largest country in Europe by area. The capital city is Stockholm. Sweden has a total population of 10.3 million of which 2.6 million have a foreign background. Persons with foreign backgrounds are defined as persons who are foreign born, or born in Sweden with foreign born parents. It has a low population density of 25 inhabitants per square kilometer (65/sq mi), with 1 437 persons per km² in localities. 87% of Swedes live in urban areas, which cover 1.5% of the entire land area.
Germanic peoples have inhabited Sweden since prehistoric times, emerging into history as the Geats (Swedish Götar) and Swedes (Svear) and constituting the sea peoples known as the Norsemen. An independent Swedish state emerged during the early 12th century. After the Black Death in the middle of the 14th century killed about a third of the Scandinavian population, the Hanseatic League threatened Scandinavia’s culture, finances and languages. This led to the forming of the Scandinavian Kalmar Union in 1397, which Sweden left in 1523. When Sweden became involved in the Thirty Years War on the Reformist side, an expansion of its territories began and eventually the Swedish Empire was formed. This became one of the great powers of Europe until the early 18th century. Swedish territories outside the Scandinavian Peninsula were gradually lost during the 18th and 19th centuries, ending with the annexation of present-day Finland by Russia in 1809. The last war in which Sweden was directly involved was in 1814, when Norway was militarily forced into a personal union, which peacefully dissolved in 1905. Since then, Sweden has been at peace, maintaining an official policy of neutrality in foreign affairs. In 2014, Sweden celebrated 200 years of peace, breaking even Switzerland’s record for peace. Sweden was formally neutral through both world wars and the Cold War, albeit Sweden has since 2009 openly moved towards cooperation with NATO.
The total resident population of Sweden was 10,343,403 in March 2020. The population exceeded 10 million for the first time on Friday 20 January 2017. The three largest cities are Stockholm, Gothenburg and Malmö. Sweden’s population has become much more ethnically, religiously and linguistically diverse over the past 70 years as a result of global immigration. Every fourth (24.9%) resident in the country has immigrant background and every third (32.3%) has at least one parent born abroad.
Society and Culture
The Culture of Sweden has long been known for the accomplishments of a wide variety of artists.
Prehistoric Sweden was the source of Norse culture, dominant in all of Scandinavia for hundreds of years, and the Temple at Uppsala in Sweden was a site of pilgrimage for Scandinavian peoples takla the Aesir. Western culture mostly recalls Vikings of Norway and Denmark for invading France, England, Scotland and Ireland, but Swedish Vikings influenced Byzantine culture, where they were known as Varangians, and are also known for founding the Kievan state.
Of the country’s many monarchs, a few of the more powerful ones, such as King Gustav III and Queen Christina, have been exceptionally important to its cultural development.
In modern times many Swedes have been internationally celebrated for their cultural work, among them Jenny Lind, PewDiePie, August Strindberg, Ingrid Bergman, Ingmar Bergman and ABBA. Automotive designs such as those of Volvo and Saab have also been widely known.
Cost of Living
The cost of living in Sweden is quite high, especially in stoclkholm, which is considered to be the far most expensive city of the country.
Stockholm is the most expensive city in Sweden. It is followed by Gothenburg and Uppsala. Cities such as Nykvarn and Södertälje are much cheaper.
Accommodation and other living costs may be higher in Stockholm and other large cities than in more rural areas. The average monthly living expenses for a student in Sweden are approximately SEK 7,070 (about 750 €).
Every day expenses fluctuate depending on where you live, but overall, the average cost of living in Sweden is high. The bulk of this high cost is due to rent prices, which climb by about 1% each year. In recent years, Sweden has experienced a housing shortage thanks to a growing demand by people flocking to the country for the high quality of life, yet not enough housing to accommodate them.
Education System
Education in Sweden is mandatory for children between ages 6 and 15. The school year in Sweden runs from mid/late August to early/mid-June. The Christmas holiday from mid-December to early January divides the Swedish school year into two terms.
Preschool is free for low-income families and subsidized with a price ceiling for all families. The year children turn six they start the compulsory preschool class (förskoleklass), which act as a transition phase between preschool and comprehensive schools. Children between ages 7 and 15 attend comprehensive school where a wide range of subjects are studied. All students study the same subjects, with exception for different language choices. The majority of schools are run municipally, but there are also privately owned schools, known as independent schools.
Almost all students continue studying in 3 year-long upper secondary schools where most students choose one out of 18 national programs some of which are vocational and some preparatory. For students not fulfilling the requirements for the national programs, introductory programs are available where students work to satisfy the requirements for the national programs. In 2018, 16% of students finishing year 9 of comprehensive school were not eligible for national programs.
The higher education system is compatible with the rest of Europe through the Bologna Process where degrees are divided into 3 cycles, basic level, advanced level and doctoral level. There are two degrees available in each cycle of different lengths. Universities have no tuition fees and student aid is available from the government.
Information Specific to International Students
The total number of foreign students in Sweden increased steadily over recent years and reached more than 400,000 in 2019. That was roughly double as much as ten years ago and made Sweden one of the leading host destinations for international students within the Europe.